NA-MIC Project Weeks
NA-MIC Project Weeks
Back to Projects List
Fine-Tuning SimCortex on Expert-Annotated Cortical Surfaces for Enhanced Topological Accuracy
Key Investigators
- Kaveh Moradkhani (École de Technologie Supérieure, Canada)
- Sylvain Bouix (École de Technologie Supérieure, Canada)
- Jarrett Rushmore (Boston University Medical, USA)
Project Description
SimCortex is a deep-learning framework that reconstructs all four cortical surfaces (left/right white matter and pial) from T1-weighted MRI, with a focus on minimizing inter-surface collisions and self-intersections while maintaining high geometric fidelity. To improve robustness and generalization, we fine-tune SimCortex—originally trained on FreeSurfer-generated segmentations—using a set of 50 expert-annotated MRI volumes.
Objectives
-
Fine‐tune SimCortex with high‐quality, manually labeled data
Fine-tune the pre‐trained SimCortex model using 50 expert‐annotated MRI segmentations to improve anatomical accuracy and reduce geometric artifacts. -
Compare fine‐tuned variants against the baseline
Evaluate several fine‐tuned configurations using geometric metrics (Chamfer Distance, ASSD, HD) and topological consistency (SIF), and compare them to the baseline SimCortex model. -
Visually validate reconstructions in 3D Slicer
Load predicted cortical surfaces into 3D Slicer and assess anatomical plausibility with expert guidance.
Approach and Plan
- Preprocessing: Convert expert-segmented MRI volumes into a format compatible with SimCortex.
- Model Fine-Tuning: Use manual segmentations to fine-tune the original SimCortex model.
- Evaluation: Measure Chamfer, ASSD, HD, and %SIF for each configuration.
- Baseline Comparison: Compare all metrics with the baseline SimCortex model.
- Expert Review: Collaborate with Prof. Jarrett Rushmore for visual validation.
- Selection: Choose the best configuration based on both quantitative metrics and expert review.
Progress and Next Steps
We fine-tuned the pre-trained SimCortex model (SimCortex_M) using 50 high-quality, expert-annotated MRI segmentations. The model was evaluated against the original SimCortex baseline using geometric and topological metrics, including Chamfer Distance, Hausdorff Distance (HD), Average Symmetric Surface Distance (ASSD), and Self-Intersection Fraction (SIF).
Both quantitative and visual evaluations demonstrate the benefits of fine-tuning:
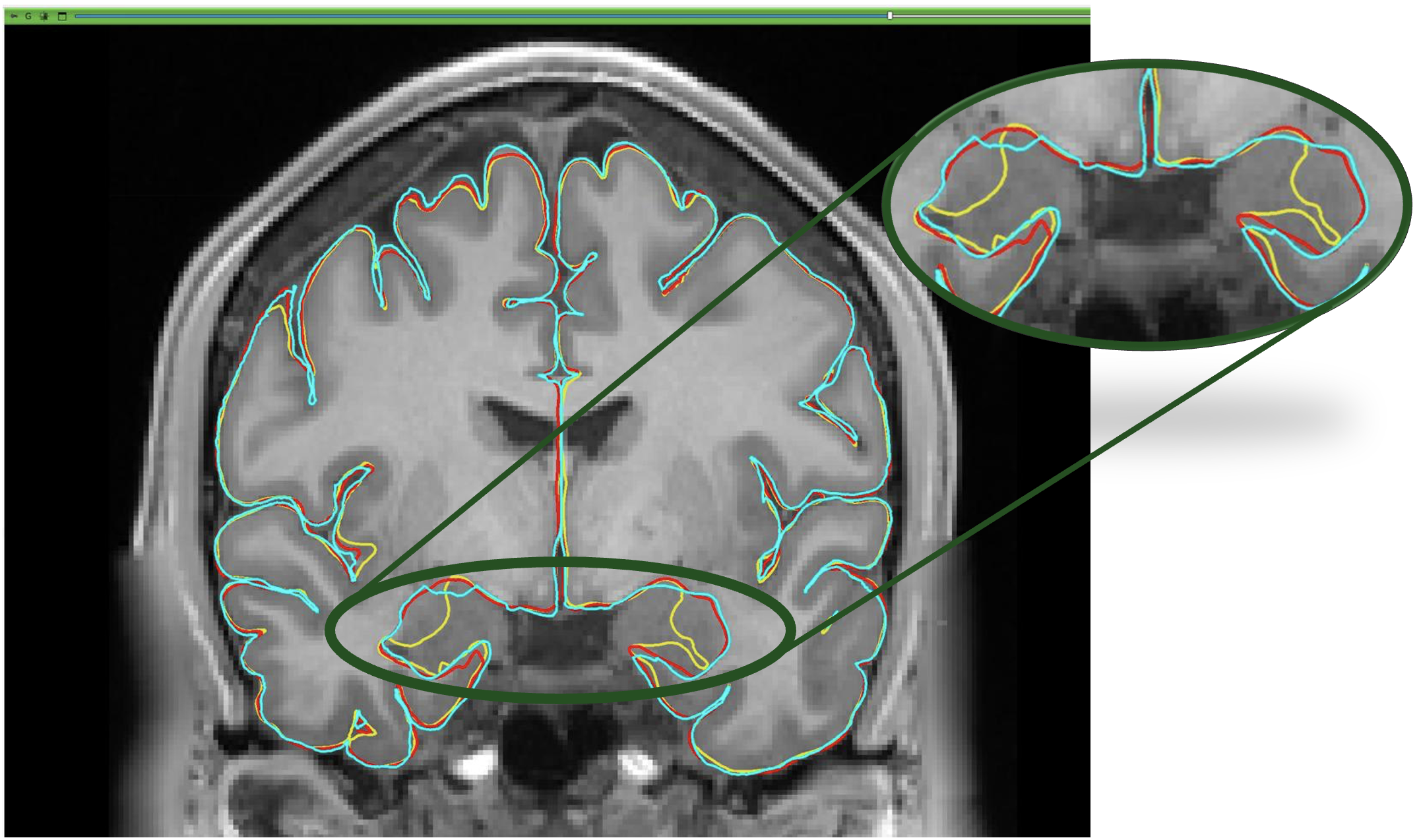
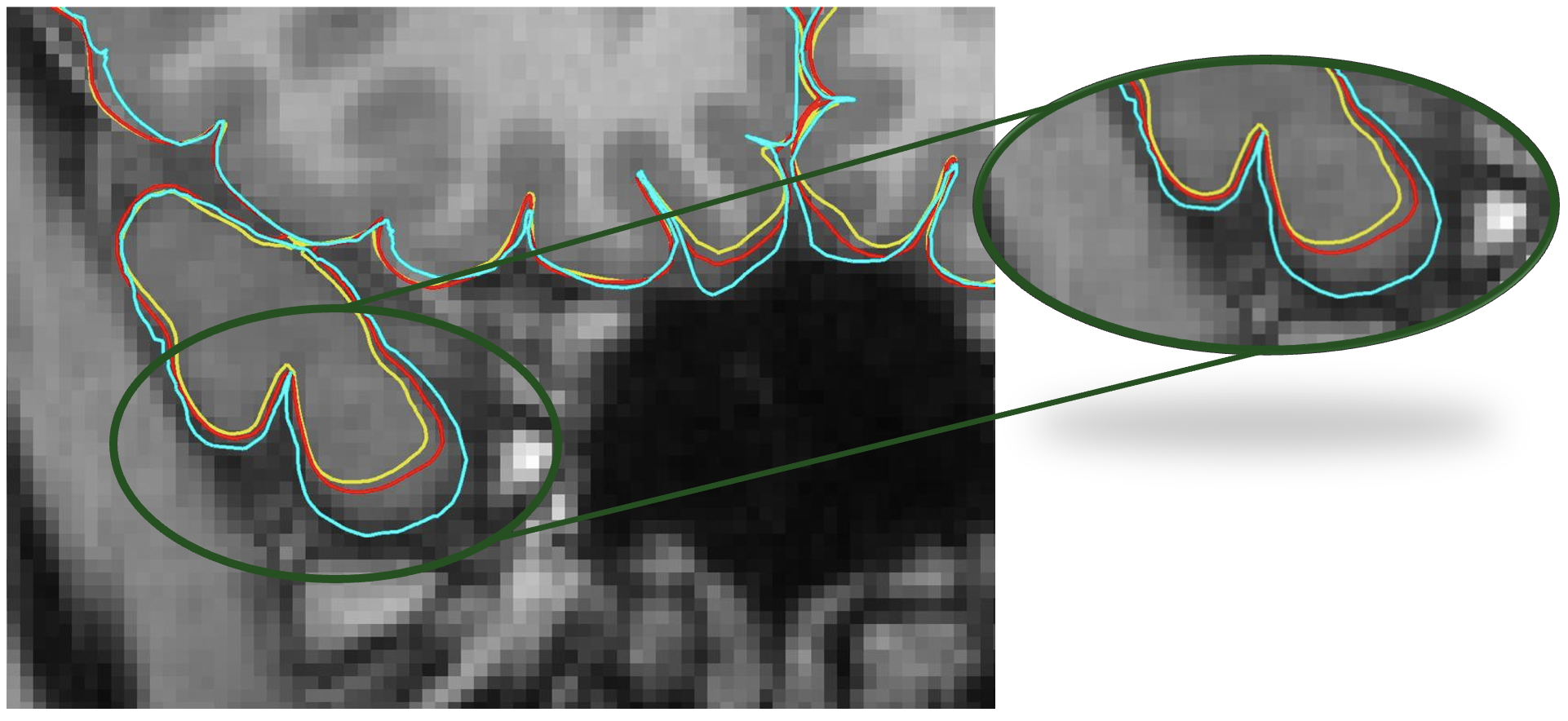
SimCortex_Machieves lower errors across all evaluated metrics.- The red surface (fine-tuned) shows better alignment with the turquoise manual ground truth, while the yellow surface (baseline) exhibits greater deviation.
- These results confirm that using expert-labeled data leads to improved anatomical and topological accuracy.
🚀 Future Direction
-
As a next step, we plan to develop a more robust version of SimCortex as a 3D Slicer extension. This extension will aim to produce more accurate cortical surfaces with minimal inter-surface collisions and eliminate self-intersections, enhancing its usability for both clinical and research workflows.
Illustrations
📊 Quantitative Evaluation Results
The table below compares baseline and fine-tuned model performance across all surfaces.

🧠 Visual Comparison of Cortical Surfaces
This Figure illustrates the differences between ground truth and predictions.
- Cyan: Manual ground truth
- Red: Fine-tuned model (SimCortex_M)
- Yellow: Baseline model (SimCortex)
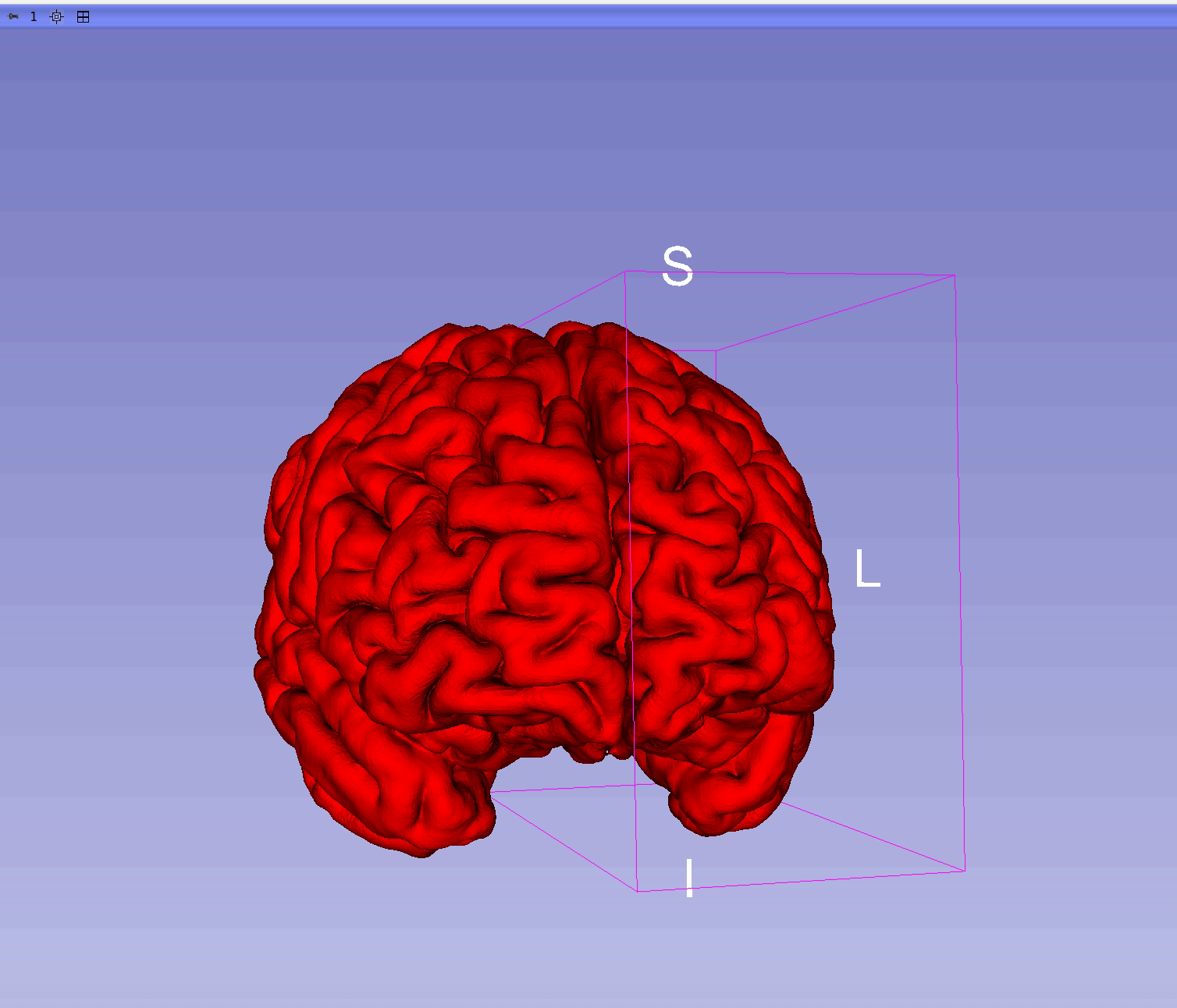
🧩 Full Brain View
🔍 Zoomed-In View
🧠 Reconstructed Cortical Surfaces (Fine-Tuned Model)